Flink状态管理与checkpoint容错机制(二) | 字数总计: 2.1k | 阅读时长: 10分钟 | 阅读量: |
状态分类 Flink支持两种状态Keyed State和Operator State。两类状态又都包括原始状态row state和托管状态managed state。
原始状态:由用户自行管理状态具体的数据结构,框架在做checkpoint的时候,使用byte[]来读写状态内容,对其内部数据结构一无所知。当实现一个用户自定义的operator时,会使用到原始状态
托管状态是由Flink框架管理的状态,通常在DataStream上的状态推荐使用托管的状态。
Keyed State 该类状态是基于KeyedStream上的状态,这个状态是根据特定的key绑定的,对keyedStream流上的每一个key,都对应着一个state。stream.keyBy(...)
数据结构:
ValueState: 即类型为T的单值状态。这个状态与对应的key绑定,是最简单的状态了。它可以通过update方法更新状态值,通过value()方法获取状态值
ListState: 即key上的状态值为一个列表。可以通过add方法往列表中附加值;也可以通过get()方法返回一个Iterable来遍历状态值。
ReducingState:这种状态通过用户传入的reduceFunction,每次调用add方法添加值的时候,会调用reduceFunction,最后合并到一个单一的状态值。
MapState<UK, UV>:即状态值为一个map。用户通过put或putAll方法添加元素。
通过value()获取值,通过update()更新值,Keyed State继承RichFunction类
private static int sourceCount = 0 ;public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception { StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment(); env.setStateBackend(new FsStateBackend ("file:///D://hadoop//data//checkpoint" )); env.getCheckpointConfig().setCheckpointingMode(CheckpointingMode.EXACTLY_ONCE); env.getCheckpointConfig().setCheckpointInterval(1000 ); DataStream<Tuple3<Integer, String, Integer>> source = env.addSource(new KeyedStateSource ()); source.keyBy(0 ) .window(TumblingProcessingTimeWindows.of(Time.seconds(2 ))) .apply(new KeyedStateRichFunction ()); env.execute(); } private static class KeyedStateSource implements SourceFunction <Tuple3<Integer, String, Integer>> { private Boolean isRunning = true ; private int count = 0 ; @Override public void run (SourceContext<Tuple3<Integer, String, Integer>> sourceContext) throws Exception { while (isRunning){ for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { sourceContext.collect(Tuple3.of(1 ,"ahah" ,count)); count++; } if (count>100 ){ System.out.println("err_________________" ); throw new Exception ("123" ); } sourceCount = count; Thread.sleep(2000 ); } } @Override public void cancel () { } } private static class KeyedStateRichFunction extends RichWindowFunction <Tuple3<Integer,String,Integer>, Integer, Tuple, TimeWindow> { private transient ValueState<Integer> state; private int count = 0 ; @Override public void apply (Tuple tuple, TimeWindow timeWindow, Iterable<Tuple3<Integer, String, Integer>> iterable, Collector<Integer> collector) throws Exception { count=state.value(); for (Tuple3<Integer, String, Integer> item : iterable){ count++; } state.update(count); System.out.println("windows count:" +count+" all count:" + sourceCount); collector.collect(count); } @Override public void open (Configuration parameters) throws Exception { ValueStateDescriptor<Integer> descriptor = new ValueStateDescriptor <Integer>( "average" , TypeInformation.of(new TypeHint <Integer>() {}), 0 ); state = getRuntimeContext().getState(descriptor); } }
代码详情:
加载数据源,每次count=10休眠2s,当达到count=100时中断数据源,重新开始…
并把window窗口大小设置2s负责触发计算,观察每次throw exception后,能不能从之前的结果开始算…
输出:
all count:10 source count:10 all count:20 source count:20 all count:30 source count:30 all count:40 source count:40 all count:50 source count:50 all count:60 source count:60 all count:70 source count:70 all count:80 source count:80 all count:90 source count:90 all count:100 source count:100 err_________________ all count:110 source count:10 all count:120 source count:20
从结果可以看出达到了想要的效果,all count的值并没有从0开始计算,而是从之前的结果计算。
Operator State 该类State与key无关,整个operator对应一个state,该类State没有Keyed Key支持的数据结构多,仅支持ListState。举例来说,Flink中的Kafka Connector,就使用了operator state。它会在每个connector实例中,保存该实例中消费topic的所有(partition, offset)映射。
有两种方式:
CheckpointedFunction(很少使用,需要自己初始化) void snapshotState (FunctionSnapshotContext context) throws Exception;void initializeState (FunctionInitializationContext context) throws Exception;
public class BufferingSink implements SinkFunction <Tuple2<String, Integer>>, CheckpointedFunction { private final int threshold; private transient ListState<Tuple2<String, Integer>> checkpointedState; private List<Tuple2<String, Integer>> bufferedElements; public BufferingSink (int threshold) { this .threshold = threshold; this .bufferedElements = new ArrayList <>(); } @Override public void invoke (Tuple2<String, Integer> value) throws Exception { bufferedElements.add(value); if (bufferedElements.size() == threshold) { for (Tuple2<String, Integer> element: bufferedElements) { } bufferedElements.clear(); } } @Override public void snapshotState (FunctionSnapshotContext context) throws Exception { checkpointedState.clear(); for (Tuple2<String, Integer> element : bufferedElements) { checkpointedState.add(element); } } @Override public void initializeState (FunctionInitializationContext context) throws Exception { ListStateDescriptor<Tuple2<String, Integer>> descriptor = new ListStateDescriptor <>( "buffered-elements" , TypeInformation.of(new TypeHint <Tuple2<String, Integer>>() {})); checkpointedState = context.getOperatorStateStore().getListState(descriptor); if (context.isRestored()) { for (Tuple2<String, Integer> element : checkpointedState.get()) { bufferedElements.add(element); } } } }
ListCheckpointed(常用,Flink自动初始化) List<T> snapshotState (long checkpointId, long timestamp) throws Exception; void restoreState (List<T> state) throws Exception;
仅支持list state,ListCheckpointed是CheckpointedFunction的限制版,它仅仅支持Even-splitredistribution模式的list-style state。ListCheckpointed定义了两个方法,分别是snapshotState方法及restoreState方法;snapshotState方法在master触发checkpoint的时候被调用,用户需要返回当前的状态,而restoreState方法会在failure recovery的时候被调用,传递的参数为List类型的state,方法里头可以将state恢复到本地.
private static int sourceCount = 0 ;public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception{ StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment(); env.setStateBackend(new FsStateBackend ("file:///D://hadoop//data//checkpoint" )); env.getCheckpointConfig().setCheckpointingMode(CheckpointingMode.EXACTLY_ONCE); env.getCheckpointConfig().setCheckpointInterval(1000 ); DataStream<Tuple4<Integer,String,String,Integer>> source = env.addSource(new OperatorStateSource ()); source.keyBy(0 ) .window(TumblingProcessingTimeWindows.of(Time.seconds(2 ))) .apply(new OperatorStateAppy ()); env.execute("" ); } private static class OperatorStateSource extends RichSourceFunction <Tuple4<Integer,String,String,Integer>> implements ListCheckpointed <UserState>{ private int count = 0 ; private boolean is_running = true ; @Override public List<UserState> snapshotState (long l, long l1) throws Exception { List<UserState> userStateList = new ArrayList <>(); UserState state = new UserState (); state.setCount(count); userStateList.add(state); return userStateList; } @Override public void restoreState (List<UserState> list) throws Exception { count = list.get(0 ).getCount(); System.out.println("OperatorStateSource restoreState: " +count); } @Override public void run (SourceContext<Tuple4<Integer, String, String, Integer>> sourceContext) throws Exception { while (is_running){ for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) { sourceContext.collect(Tuple4.of(1 , "hello-" + count, "alphabet" , count)); count++; } sourceCount = count; Thread.sleep(2000 ); if (count>=100 ){ System.out.println("err_________________" ); throw new Exception ("exception made by ourself!" ); } } } @Override public void cancel () { is_running = false ; } } private static class OperatorStateAppy implements WindowFunction <Tuple4<Integer,String,String,Integer>,Integer,Tuple,TimeWindow>,ListCheckpointed<UserState>{ private int total = 0 ; @Override public List<UserState> snapshotState (long l, long l1) throws Exception { List<UserState> userStateList = new ArrayList <>(); UserState state = new UserState (); state.setCount(total); userStateList.add(state); return userStateList; } @Override public void restoreState (List<UserState> list) throws Exception { total = list.get(0 ).getCount(); } @Override public void apply (Tuple tuple, TimeWindow timeWindow, Iterable<Tuple4<Integer, String, String, Integer>> iterable, Collector<Integer> collector) throws Exception { int count = 0 ; for (Tuple4<Integer,String,String,Integer> data:iterable){ count ++; } total = total + count; System.out.println("all count:" +total+" source count:" + sourceCount); collector.collect(total); } } static class UserState implements Serializable { private int count; public int getCount () { return count; } public void setCount (int count) { this .count = count; } }
输出:
all count:10 source count:10 all count:20 source count:20 all count:30 source count:30 all count:40 source count:40 all count:50 source count:50 all count:60 source count:60 all count:70 source count:70 all count:80 source count:80 all count:90 source count:90 all count:100 source count:100 err_________________ OperatorStateSource restoreState: 100 all count:110 source count:110
从结果可以看出达到了想要的结果,当数据源中断后,调用了restore方法,恢复了state的值。
总结:
两者的区别,实现CheckpointedFunction接口,有两种形式的ListState API可以使用,分别是getListState以及getListUnionState,它们都会返回一个ListState,但是他们在重新分区的时候会有区别,后面会详细介绍。如果我们直接实现ListCheckpointed接口,那么就会规定使用ListState,不需要我们进行初始化,Flink内部帮我们解决。
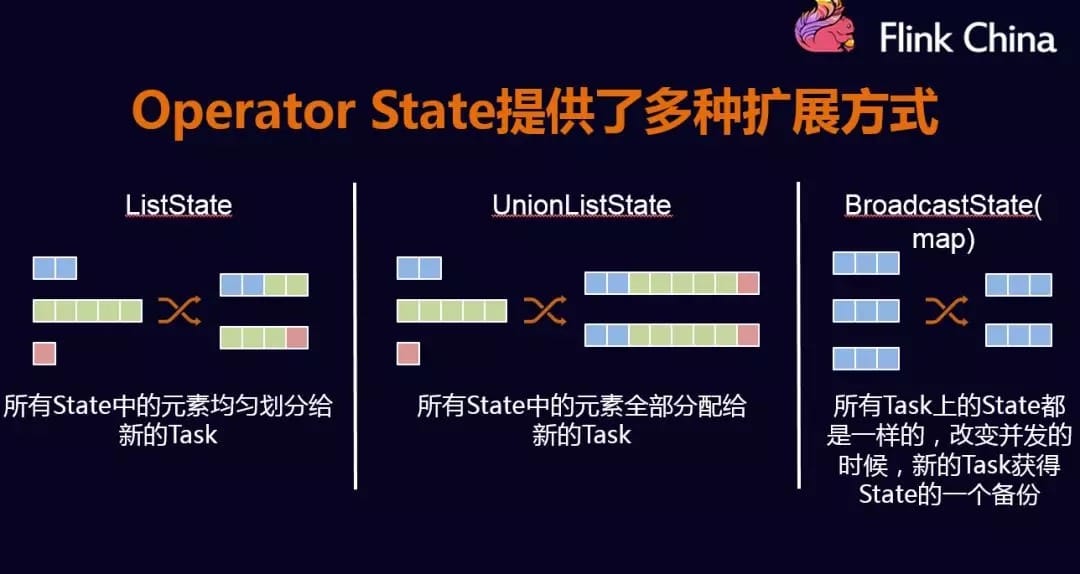
state重分区 当我们在一个job中重新设置了一个operator的并行度之后,之前的state该如何被分配呢?下面就ListState、ListUnionState以及BroadcastState来说明如何进行重分区。
原文:https://github.com/heibaiying/BigData-Notes