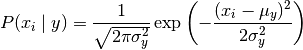import numpy as np
from sklearn.utils import array2d
from sklearn.utils.extmath import logsumexp
import random
import matplotlib.pylab as plt
class GaussianBayes:
def __init__(self):
pass
def train(self, x, y):
n_samples, n_features = x.shape
if(n_samples != y.shape[0]):
raise ValueError('x and y have incompatible shapes.')
self._classes = unique_y = np.unique(y)
n_classes = unique_y.shape[0]
self._theta = np.zeros((n_classes, n_features))
self._sigma = np.zeros((n_classes, n_features))
self._class_prior = np.zeros(n_classes)
epsilon = 1e-9
for i, y_i in enumerate(unique_y):
self._theta[i, :] = np.mean(x[y == y_i, :], axis = 0)
self._sigma[i, :] = np.var(x[y == y_i, :]) + epsilon
self._class_prior[i] = np.float(np.sum(y == y_i)) / n_samples
return self
def predict(self, x):
prob = self.predict_proba(x)
indexs = []
scores = []
for ele in prob:
index = np.argmax(ele)
score = ele[index]
indexs.append(index)
scores.append(score)
return [indexs, scores]
def predict_log_prob(self, x):
joint = self.joint_log_likelihood(x)
log_like_x = logsumexp(joint, axis = 1)
return joint - np.atleast_2d(log_like_x).T
def predict_proba(self, x):
return np.exp(self.predict_log_prob(x))
def joint_log_likelihood(self, x):
x = array2d(x)
joint_log_likelihood = []
for i in xrange(np.size(self._classes)):
jointi = np.log(self._class_prior[i])
n_ij = - 0.5 * np.sum(np.log(np.pi * self._sigma[i, :]))
n_ij -= 0.5 * np.sum(((x - self._theta[i, :]) ** 2) /
(self._sigma[i, :]), 1)
joint_log_likelihood.append(jointi + n_ij)
joint_log_likelihood = np.array(joint_log_likelihood).T
return joint_log_likelihood
def samples(n_samples, n_features = 10, classes = 5, rat = 0.2):
x = np.zeros((n_samples, n_features))
y = np.zeros((n_samples, 1))
num = int(n_samples / classes)
for i in range(0, classes):
x[i*num:i*num + num] = np.random.random((num,n_features)) + i
for i in range(0, x.shape[0]):
y[i, 0] = int(i / num)
index = np.arange(0, x.shape[0])
random.shuffle(index)
train_index = index[0: int((1-rat) * x.shape[0])]
test_index = index[int((1-rat) * x.shape[0]):-1]
train_x = x[train_index, :]
train_y = y[train_index]
test_x = x[test_index, :]
test_y = y[test_index]
return [train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y]
def plotRes(pre, real, test_x):
s = set(pre)
col = ['r','b','g','y','m']
fig = plt.figure()
pre = np.array(pre)
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
for i in range(0, len(s)):
index1 = pre == i
index2 = real == i
x1 = test_x[index1, :]
x2 = test_x[index2, :]
ax.scatter(x1[:,0],x1[:,1],color=col[i],marker='v',linewidths=0.5)
ax.scatter(x2[:,0],x2[:,1],color=col[i],marker='.',linewidths=12)
plt.title('The prediction of the Gaussian Bayes')
plt.legend(('c1:predict','c1:true',
'c2:predict','c2:true',
'c3:predict','c3:true',
'c4:predict','c4:true',
'c5:predict','c5:true'), shadow = True, loc = (0.01, 0.4))
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
[train_x, train_y, test_x, test_y] = samples(2000, 30, 5)
gb = GaussianBayes()
gb.train(train_x, train_y)
pred_y = gb.predict(test_x)
plotRes(pred_y[0], test_y.ravel(), test_x)
|